Crypto wallets are essential tools for managing digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies. They play a key role in securely storing and accessing funds. Understanding these wallets, particularly the differences between hot and cold types, is crucial for protecting digital investments.
What Are Crypto Wallets?
A crypto wallet is a specialized tool designed for securely storing, managing, and accessing cryptocurrency. Instead of holding physical currency, it stores private keys—unique codes that grant access to funds on the blockchain. Proper management of these wallets is essential to prevent unauthorized access or the loss of funds.
The Importance of Private Keys in Crypto Wallets
Private keys are the foundation of any cryptocurrency wallet. They authorize transactions and verify ownership. Losing access to your private keys or exposing them to threats can lead to irreversible loss, as cryptocurrency systems are decentralized and lack recovery mechanisms.
Types of Crypto Wallets: Hot Wallets and Cold Wallets
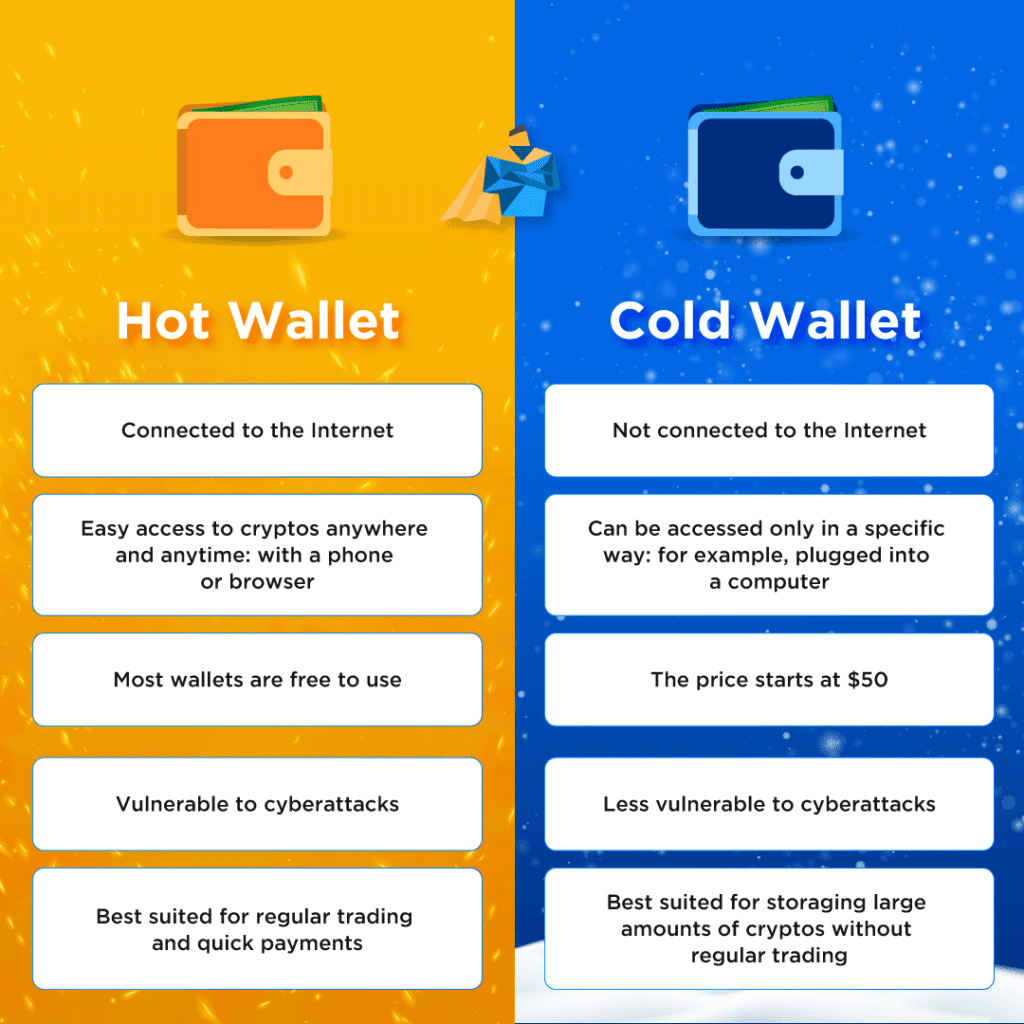

Cryptocurrency wallets can be broadly divided into two types:
- Hot Wallets: Always connected to the internet, these wallets are ideal for frequent transactions.
- Cold Wallets: Offline storage options prioritize security and are suited for long-term storage.
Choosing the right type of wallet depends on your usage patterns and security needs.
Hot Wallets for Accessibility
Hot wallets are popular for their convenience and easy accessibility. However, their internet connectivity makes them more susceptible to cyber threats.
Examples of Hot Wallets:
- Mobile Apps: Applications like MetaMask and Trust Wallet for managing assets on the go.
- Desktop Software: Tools such as Exodus and Electrum for secure access on computers.
- Web-Based Platforms: Wallets integrated with services like Coinbase or Binance.
Benefits of Hot Wallets:
- Instant access to funds.
- Seamless integration with trading platforms.
- Beginner-friendly features.
Drawbacks of Hot Wallets:
- Increased vulnerability to hacking and phishing attacks.
- Requires internet access, posing additional risks.
Cold Wallets for Maximum Security
Cold wallets are offline solutions that provide robust security for cryptocurrency holdings. Designed for long-term storage, they minimize exposure to online threats.
Examples of Cold Wallets:
- Hardware Devices: Gadgets like Ledger and Trezor that store private keys offline.
- Paper-Based Solutions: Documents containing printed keys or QR codes.
- Isolated Systems: Air-gapped devices for secure key storage.
Advantages of Cold Wallets:
- Protection from online hacking and malware.
- Suitable for safeguarding large holdings over extended periods.
- Full control over private keys without reliance on third parties.
Disadvantages of Cold Wallets:
- Loss or damage can render funds inaccessible.
- Higher initial cost for hardware options.
How to Choose the Best Crypto Wallet
The best wallet depends on your needs. Hot wallets are ideal for frequent transactions, while cold wallets offer superior security for long-term storage. Understanding how wallets work and their specific advantages will help you protect your digital assets and manage investments with confidence.



